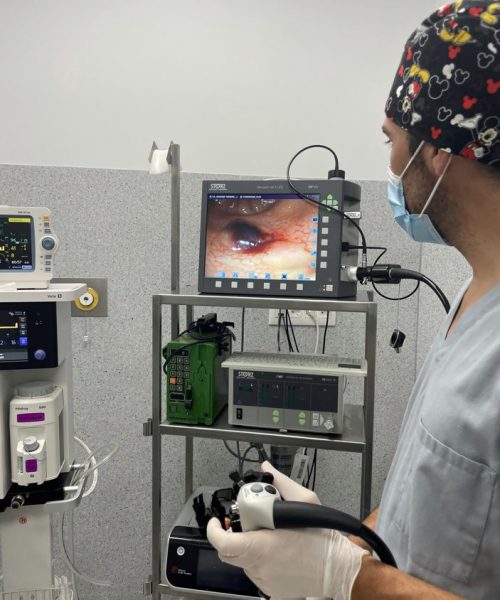
What is endoscopy?
Endoscopy is a procedure in which our veterinarians at NA Veterinary Hospital en Jerez de la Frontera introduce a tube incorporating a camera and a light source through the body’s natural orifices, such as the respiratory tract or the intestinal tract, or through surgical incisions in, for example, the abdominal cavity or a joint, to observe internal body cavities. It can also incorporate instruments to perform sampling or minimally invasive surgical interventions at the same time (cauterisation of tissues, removal of cysts, polyps or tumours…).
Endoscopy requires anaesthesia and therefore does not cause any pain or trauma for the patient. It can be used to explore the nose, ears, digestive system, respiratory system, reproductive system and urinary system.
When should endoscopy be considered?
It is recommended for understanding the cause of sneezing, vomiting, diarrhoea or urinary problems in pets and can be used to remove objects from the nose, lungs, stomach or oesophagus without painful surgery.
Recovery time is immediate, so once it is done, the pet can resume its daily life right away.
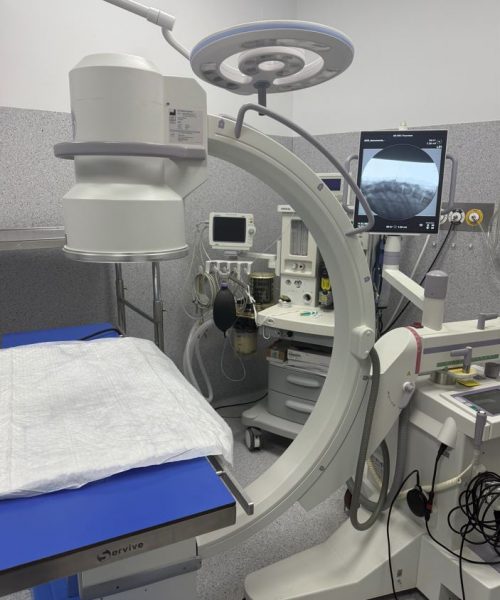
What is Fluoroscopy?
Fluoroscopy is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses X-rays to create real-time, moving images from inside the body. Unlike a conventional X-ray, which is like a “still photograph”, fluoroscopy is like a “video” of what’s happening inside the organism.
Specialised X-ray equipment is used, often with a C-arm (which allows the X-ray generator and detector to move around the patient). The X-rays pass through the animal’s body and are captured by a detector that converts the information into digital images displayed on a monitor.
When is Fluoroscopy Considered?
It’s recommended for assessing how an animal swallows (dysphagia), the passage of food through the digestive system, or for diagnosing tracheal or bronchial collapse, as these conditions are only evident when seen in motion. Furthermore, it’s essential for guiding procedures such as the exact placement of implants in orthopaedic surgeries, the removal of foreign bodies without the need for open surgery, or the precise insertion of catheters and stents in delicate systems like the cardiac, urinary, or respiratory tracts.
